TYPES OF RETAIN WALLS
INTRODUCTION
Retaining walls these are relatively rigid walls
designed and constructed for provision of support to soil masses laterally, so
that will be prevented from sliding or eroded away.
Why we need retain walls or retaining
structures
On sloping land of earth surface the soil is not
stable, lateral forces push soil masses by sliding or eroding form upper land
to lower land.
Soil is stable when the slope of the surface is
flatter than safe slope, on sliding the soil is trying to flatten its surface,
when we have limited space it not possible to provide the safe slope and soil
is to be retained at a slope steeper than the safe one, here retaining
structures comes.
Retaining wall can be found in bridges, buildings,
flyovers and roads.
Types of retaining walls
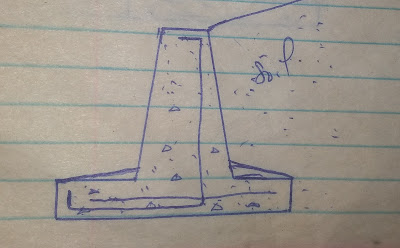
1. Gravity retaining wall
These are retaining walls which their stability against lateral forces from soil mass depend on their weight, usually constructed from plain concrete or masonry, this kind of retaining wall is not economical as it uses a lot material.
2. Semi gravity retaining wall
In this type of retaining wall, small amount of reinforcement is introduced inside the concrete; the introduced reinforcements near the back face reduce the size of retaining wall and cracks formation.
3. Cantilever retaining wall
These are retaining walls made of reinforced concrete which consist of thin stem and a base which casted monolithically, this is the modification of gravity retaining walls where by introduction of reinforcement reduces wall side to an acceptable one.
4. Counterfort retaining wall
In this types of retaining wall thin
vertical slabs (counter-forts) spaced across the vertical step at regular
interval, the counter forts tie the vertical stem with base slabs span between
the counterforts.
The purpose of providing counter fort is to reduce shear forces and bending moments in the vertical stem.
5. Anchored retaining wall
These are retaining walls which are held or supported by cables or wires driven deep sideway into the earth and anchored at their ends.
The anchored cables act against lateral forces which could lead to sliding or overturning, as cables support the wall then then the thickness of wall can be reduced to certain percent.
6. Sheet piling retaining wall
These are retaining walls made by driving piles or sheets into the soil to a certain depth that they can resist lateral forces.
The piles or sheets mostly are driven up to about 1/3 of pile height so as to have required stability, in most cases this type of retaining walls are applied for temporal purposes.
Conclusion
On sloping land of earth surface the soil is not stable, lateral forces push soil masses by sliding or eroding form upper land to lower land in order to flatten their surface for stability, retain wall introduced to resist the lateral forces at minimum space.









Comments
Post a Comment