FIELD DENSITY BY SAND CONE REPLACEMENT METHOD
Objective of the test
This is in situ test which is used to determine the degree of compaction of the road layers (lower layers) such as subgrade, subbase layers or any compacted fill such as embarkment or backfill.
In situ activities help to determine bulk density of compacted material of road layer, accompanied with moisture determination at laboratory, both results used in dry density calculation.
Main Principles
Clean, graded and dry sand of known density is used in volume determination of excavated hole.
Equipment and Materials required
- Sand cone apparatus
- Weight balance readable to 1g
- Density plates
- Scoop
- Moisture container
- Digging tools
- Dry sand of known density
- Brush
Test procedures
- The locations to be tested are selected systematically or randomly as desired or proposed by engineer.
- Weigh calibrated sand cone apparatus full of dry sand of known density as W1.
Weighing calibrated sand cone apparatus full of sand - Seat tightly density plate on levelled and clear test ground location.
- Dig out soil by referring size of density plate hole to desired depth of road layer.
Digging out of selected location on road layer - Collect excavated soil and weigh it, W3 small amount of excavated soil of about 400g then is taken for moisture determination.
- Put sand cone apparatus full of dry sand on density plate, open valve to allow sand to fill the hole, when sand stops flowing valve is closed and apparatus is removed.
- Weigh sand cone apparatus with remaining sand as W2.
- Collect all possible sand from hole and fill back the hole with excavated material.
Calculation and Report
Determination of volume of excavated hole (volume of excavated material on compacted road layer)
From bulk density and determined moisture content, dry density can be calculated.
Degree of compaction is calculated by dividing calculated dry density with design maximum dry density multiplied by 100%.


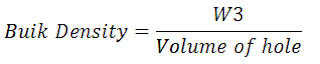





Comments
Post a Comment