PRINCPLE PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
PRINCPLE PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
Fluids
is the substance that deform continuously under shearing force, also these are substances that can flow include liquid and gas.
Fluid mechanics is the study which deals with
fluids, their properties and forces on them.
Fluids have three major properties which are
- Density
- Viscosity
- Surface tension
These are very important properties to be discussed
so as to know how fluids behave in different situations.
Density
This is the quantity of substance present in it per
unit volume, density of substances can be expressed in different ways as follows
This is the mass of the substance per unit volume; mass density is expressed in kilogram per cubic meter as kg/m3.
2. Unit weight of specific weight
This is quantity of substance in Newton per unit volume; unit weight is expressed in Newton per cubic meter.
3. Relative density
Relative density is the ratio of quantity of
substance per unit volume to the quantity of standard liquid of equal volume at
standard temperature (standard liquid is water at 4⁰C).
Relative density has no SI Unit as it is ratio of
two densities.
Viscosity
Viscosity is the fluid property due to cohesion and
interaction between fluid molecules.
Viscosity offers resistance of fluid to flow or stir
or pour, it is the measure of fluidity of the fluid.
Viscosity of fluid can be expressed in the following terms
1. Coefficient of dynamic viscosity μ
This expresses the amount of shear stress required for producing certain amount of shear strain.
2. Coefficient of kinematic viscosity v
Is the ration between coefficients of dynamic viscosity to density of the fluid.
Surface tension
Surface tension this is the property of fluid
surface to offer resistance against tension, this property is caused by strong
cohesion between liquid molecules and weak adhesion between liquid and air
molecules.
If we would have strong adhesion between liquid and
air molecules and weak cohesion between liquid molecules, then we would see
that liquid molecules are dispersed into air.
This property bring about formation of meniscuses of
liquids as they can be seen in narrow tubes
In first tube we have concave meniscus which is formed, because we have weak adhesion between liquid molecules and strong adhesion between liquid and tube molecules.
In second tube we have convex meniscus which is formed, because we have strong cohesion between liquid molecules and weak adhesion between liquid and tube molecules.
In construction effect of surface tension can be seen Bulking of the sand as water film formed around sand particles, its surface tension tends to push sand particles apart.
Capillarity
This property of fluid to rise or fall through
narrow tube, this is caused by surface tension on the surface of the liquid
which tends to drag liquid up or down through narrow tube following its
direction.
In this property we have two kinds of effects
capillary rise and capillary fall.
Capillary rise
This is the rise of liquid above its surface through
narrow tube. This is caused by positive direction of surface tension as shown
in A.
In A angle of contact between surface tension and
vertical is acute so it pulls liquid upward, in the following manner.
Force pulling liquid = surface Tension x cos α
(angle of contact).
Since the cos of acute angle (α < 90) is positive
then, we have positive pulling force which pulls liquid upward.
Capillary fall
This is the fall of liquid below its surface through
immersed narrow tube. This is caused by negative direction of surface tension
as shown in B.
In A angle of contact between surface tension and
vertical is obtuse so it pulls liquid downward, in the following manner.
Force pulling liquid = surface Tension x cos α
(angle of contact).
Since the cos of obtuse angle (α > 90) is
negative then, we have negative pulling force which pulls liquid downward.
In construction effect of capillary rise can be seen
as water rise from soil below or around foundation to the foundation, wall and
other structural parts.

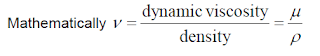





Comments
Post a Comment